A
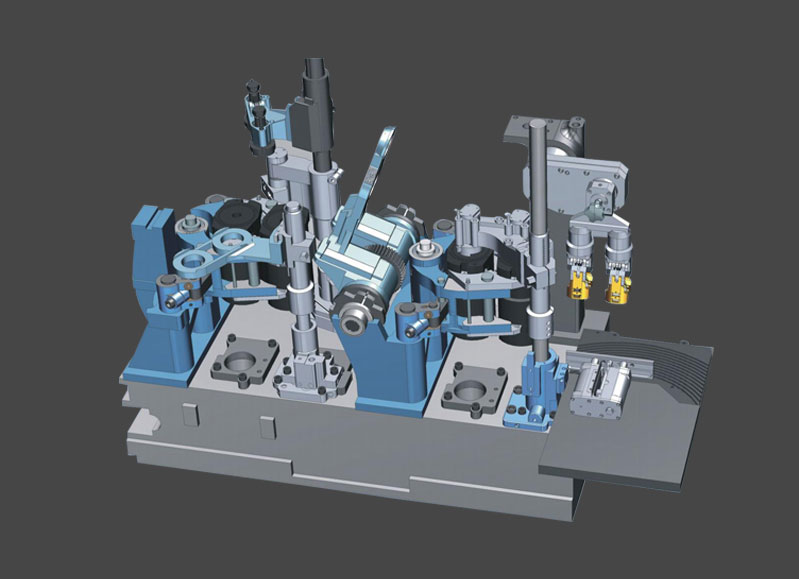
piston shaft, also known as a piston rod or piston stem, is a component found in reciprocating engines, hydraulic cylinders, and pneumatic systems. It is a cylindrical rod that connects the piston head to the crankshaft or other reciprocating mechanism.
In an internal combustion engine, the piston shaft serves as a link between the piston and the crankshaft. As the combustion process occurs, the piston moves up and down within the cylinder, and the motion is transmitted to the crankshaft through the piston shaft. This converts the linear motion of the piston into rotational motion, which ultimately drives the engine.
In hydraulic and pneumatic systems, the piston shaft is responsible for transmitting the force generated by the piston to the external load or mechanism. It transfers the linear movement of the piston to the intended application, such as lifting heavy loads or operating hydraulic machinery.
Piston shafts are usually made of sturdy materials such as steel or alloy, as they need to withstand high forces and resist wear. They are designed to be rigid and durable, ensuring reliable performance in the respective systems they are used in.
The installation process for a piston shaft can vary depending on the specific application and type of engine or system you are working with. However, I can provide you with a general overview of the steps involved in installing a piston shaft in an internal combustion engine.
Here are the basic steps for installing a piston shaft:
Preparation: Ensure you have the necessary tools and equipment for the installation. Clean the cylinder bore and piston head to remove any dirt, debris, or old gasket material. Inspect the piston shaft for any signs of damage or wear.
Lubrication: Apply a thin coat of engine oil or assembly lubricant to the piston shaft. This will reduce friction during installation and initial engine startup.
Positioning the piston: Insert the piston into the cylinder bore, aligning the connecting rod with the crankshaft journal. Use a ring compressor tool to compress the piston rings, allowing the piston to fit smoothly into the cylinder.
Installing the piston shaft: Slide the piston shaft through the cylinder bore and connect it to the connecting rod. Ensure that the piston shaft is properly aligned with the cylinder bore and the connecting rod. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines regarding torque specifications for the piston shaft bolts or nuts.
Checking clearances: Before fully tightening the piston shaft bolts or nuts, check the clearances between the piston shaft, connecting rod, and crankshaft. Ensure there is proper clearance and no interference between the components. This is especially important if the engine has been machined or modified.
Final assembly: Once the piston shaft is securely installed, proceed with the reassembly of other engine components, such as the cylinder head, intake manifold, and exhaust system, following the manufacturer's instructions.
Remember, these steps are a general guide, and the actual installation process may differ depending on the specific engine or system. It's always advisable to refer to the engine's service manual or consult a professional mechanic for precise instructions and guidance.



 English
English 中文简体
中文简体




 Jul 23,2024
Jul 23,2024
 +86-575-87637902
+86-575-87637902 +86-13606564271
+86-13606564271
 No. 20, Sanfeng Road, Diankou Town, Zhuji City, Zhejiang Province, China
No. 20, Sanfeng Road, Diankou Town, Zhuji City, Zhejiang Province, China